|
Ceramic tools have high resistance to heat and to wear and can be used to machine metals that are extremely hard, and they are chemically stable. These attributes allow them to be used to machine metals at high cutting speeds and in dry machining conditions because it is not necessary to reduce temperatures on the cutting edges of these tools. However, these favorable properties are exchanged in machining for lower toughness when these tools are compared with carbide tools. This deficiency can be offset by selecting an appropriate ceramic cutting grade and the type of tool. Ceramic tools are based primarily on alumina (Al2O3) and silicon nitride (Si3N4) compounds and are available in a variety of grades that include ceramics mixed with other materials and reinforcing whisker materials that make them harder. Oxide ceramics
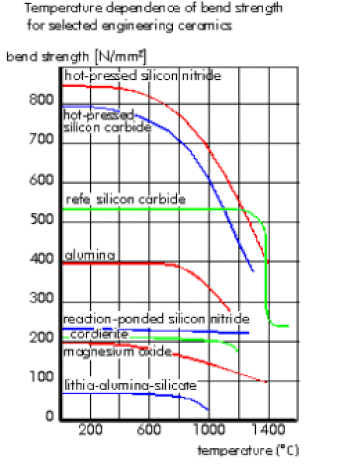
The materials are molded at pressure more than 4,000 psi and they are sintered at approximately 3,000 degrees F. This process accounts in part for the high density and hardness of these tools. Oxide ceramics are used primarily for rough and finish turning, for grooving of gray and nodular cast iron and for continuous cutting at high cutting speeds without the use of coolant. Ceramic tools are stable at extreme temperatures as high as 4,000 degrees F., unlike carbide and cement tools that contain metallic binders and begin to soften at temperatures greater than 1,000 degrees F. Whiskered ceramicsReinforced or whiskered, ceramics use extremely fine-grained silicon-carbide crystals that are called “whiskers” because they resemble small hairs under a microscope to reinforce and toughen basic ceramic compounds. In ceramic tool materials, single-crystal silicon carbide whiskers, on the order of one micron in diameter and 0.003937 in. (100 microns) in length, are intertwined within the alumina-matrix structure. These whiskers have a tensile strength of about 1 million psi and dramatically improve the fracture toughness of the tool material. They also effectively block and prevent propagation of cracks. Reinforced ceramics work differently from other cutting materials. With reinforced ceramic cutting tools, the objective in machining is to generate high temperatures ahead of the cutting tool to soften or plasticize the workpiece material. That facilitates the removal of material and a reduction in cutting forces. The ideal cutting temperature in nickel alloy is about 1,800 degrees F, for example. Cutting with ceramic inserts requires high surface speed and balanced feedrates. High speed is necessary to generate the high temperature in the shear zone and to ensure that the heat propagates into the chip-forming zone immediately ahead of the cutter. When cutting speeds are too slow, insufficient heat is generated to soften the material in this zone, and the cutting forces are raised and insert failure occurs. A strategy for using ceramic inserts is to program fewer, but deeper cuts that bury the insert deep in the workpiece. This moves the notch formation further up the face of the insert to an area that has a larger, stronger cross section. Ramping cuts should be programmed to accommodate these tools and fixed depths of cut should be avoided to spread wear over a larger section of the insert. When machining interrupted cuts with reinforced ceramics, it is important to keep the speed of the cutter high. A rule of thumb is to estimate the percentage of voids in the workpiece surface and increase cutting speed by that percentage. This increase in surface speed offsets the loss of heat generation created by the voids. Whiskered ceramics work best on hard ferrous materials and difficult-to-machine nickel-base alloys, including Inconel, Waspoloy and Hastelloy. They do not work well on ferrous alloys below Rc 42 hardness because of the chemical reaction that occurs between iron and the carbon that is part of the silicon carbide reinforcing material. Silicon nitridesCeramics based on silicon nitride offer increased resistance to abrasion and thermal shock and have high fracture toughness. These ceramic tools have a needle-like structure that is embedded in a temperature-resistant grain-boundary. These structures enhance crack deflection, crack bridging and pull-out effects, and lead to superior fracture toughness. These materials are based on compositions of ceramic powders with high purity. Techniques used to produce these ceramics, including optimized powder processing and gas-sintering, enhance their fracture toughness and high-temperature hardness. Silicon nitrides are well suited for rough machining cast iron, even under unfavorable conditions such as heavily interrupted cuts and varying depths of cut. Silicon nitrides also are used to mill cast iron, even with positive tool geometries. Silicon nitrides are suitable for milling operations that produce chips with large cross sections and require positive tool geometries. When used with powerful machine tools, silicon nitrides enable high cutting speeds (more than 800 in./min.) and feeds (0.2 to 0.3 in./min.) for rough boring cast iron. Silicone nitride tools offer fracture resistance, but their relatively low resistance to chemical wear limits their use in machining nodular cast irons. However, wear-resistant, chemical vapor deposit (CVD) alumina coatings have expanded the range of applications for silicon nitride-based tools to include these difficult-to-machine irons. Gray cast iron and nodular graphite cast iron can be milled at cutting speeds of 500 to 800 in./min or sometimes faster than 1,000 in./min. Five Types of Ceramic Cutting Tools.There are five types os ceramic cutting tools. Here are the basic differences:
ALUMINIUM OXIDE OR WHITE CERAMIC NTK GRADES: HC1, CX3, HW2 Pure alumina strengthened by Zirconium.
MIXED OR BLACK CERAMICS NTK GRADES: HC2, HC4, HC5, ZC4 Alumina with metallic phase of Titanium Carbide and Titanium Nitride which improves thermal conductivity.
SILICON NITRIDE BASED CERAMICS NTK GRADES: SX1, SX2, SX8, SP2
WHISKER REINFORCED CERAMICS NTK GRADES: WA1 Pure alumina structurally strengthens from introduction of Silicon Carbide in the form of whiskers.
SIALONS NTK GRADES: SX5 Alumina substrate strengthened by Silicon Nitride.
The above text is from American Machinist's Cutting Tool Central. For up to the minute information follow them on Twitter @AmericanMachnst
10 Comments
syed irshad ahmad qadri
7/27/2015 15:42:50
dear sir,
Reply
Deept Murti Madhav
1/28/2022 23:15:30
Dear sir,
Reply
4/2/2019 19:56:35
Thanks for helping me understand that there are silicon-carbide crystals which resemble hair which is why they are called whiskers. I just got curious about stuff like this since I heard my best friend that he needs to buy some. It appears that it is for the holes that he needs to drill from a piece of metal equipment he has to make it work again.
Reply
1/12/2021 01:27:46
You have described it so well. Thank you such a great knowledge. keep sharing!!
Reply
Ibrahim
2/14/2021 08:16:05
Kindly explain the factors considered in application of the three ceramic grade cutting tools
Reply
Md.Mohsin Sharif
10/4/2023 23:01:11
Our need black ceramic cutting tools with Manual lathe machine tools holder.
Reply
10/30/2023 01:58:11
This insightful article on ceramic cutting tools highlights the trade-offs between their exceptional heat resistance and wear durability against their lower toughness compared to carbide tools. The selection of the right ceramic grade and tool type becomes crucial to compensate for this deficiency. The exploration of oxide ceramics, enriched with elements like titanium and silicon-carbide, reveals their application in rough and finish turning, grooving, and continuous cutting without coolant. Additionally, whiskered ceramics, with fine silicon-carbide whiskers enhancing toughness, provide a fascinating solution. Considering steel fabrication, the article could delve into how these ceramic tools find utility in this domain, perhaps in precision cutting or specialized applications.
Reply
Cory
7/4/2024 19:17:34
Do they make ceramic tools for carving wood.
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
Technical Support BlogAt Next Generation Tool we often run into many of the same technical questions from different customers. This section should answer many of your most common questions.
We set up this special blog for the most commonly asked questions and machinist data tables for your easy reference. If you've got a question that's not answered here, then just send us a quick note via email or reach one of us on our CONTACTS page here on the website. AuthorshipOur technical section is written by several different people. Sometimes, it's from our team here at Next Generation Tooling & at other times it's by one of the innovative manufacturer's we represent in California and Nevada. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
About
|
© 2024 Next Generation Tooling, LLC.
All Rights Reserved Created by Rapid Production Marketing
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
