|
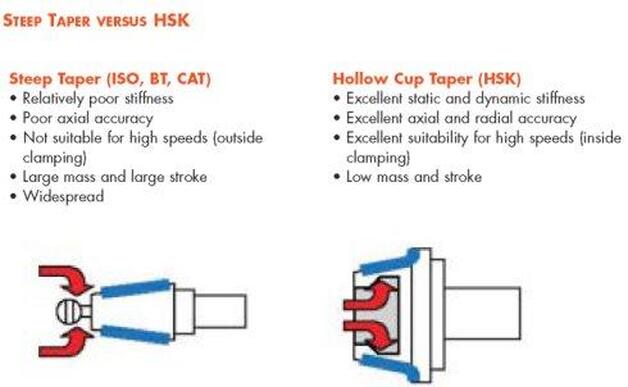
edited by Bernard Martin As machining spindle speeds have increased, steep taper rotary toolholders like BT and CAT systems tend to lose accuracy due to higher centrifugal when running at high RPM's. The mouth of the machining center spindle can grow and eventually "bell mouth" with these older style steep taper holders. As it grows the BT and CAT tool is under constant drawbar pull, is pulled up deeper inside the expanded spindle taper. This causes the Z-axis offset to change and can lead the toolholder getting stuck in the spindle. Major Differences between Steep Taper and HSKThere are several major differences between "steep taper" toolholders, like NMTB, CAT & BT and HSK.
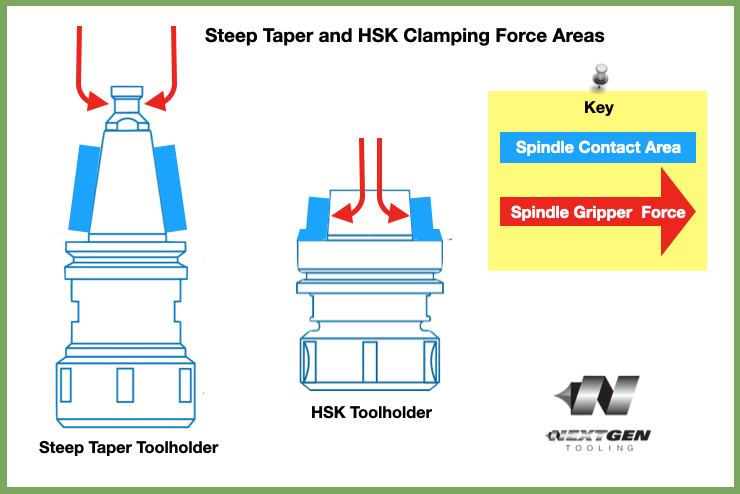
Dual ContactOne of the big differences between HSK, short taper toolholders is the way the tool fits into the machine tool spindle. HSK uses a simultaneous fit between the short taper and the face of the spindle. The connection is very rigid. HSK provides dual contact between the spindle face and taper while a conventional V-taper only makes taper contact. A standard steep V-taper tool system is designed to make contact along a fixed taper in the machining center spindle. The tool is held firm against this taper by the drawbar inside the spindle of your CNC. When a conventional holder is seated in the CNC spindle, there is approximately a 3 mm gap between the tool holder flange and the spindle face. HSK is short for the German words "Hohl Shaft Kegel" or, in English, Hollow Shank Taper because of how the tool is held in the spindle. 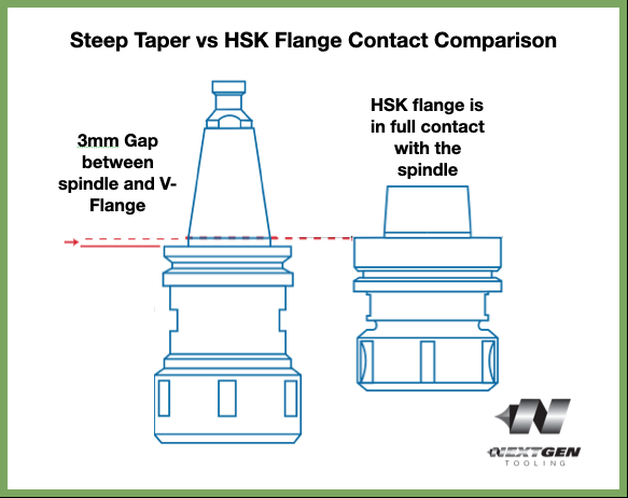 Note how HSK taper (right) is a dual-contact taper. Meaning that it is flush with the gauge line of the spindle face, creating dual contact between the flange of the holder and the spindle face, and the taper itself and the spindle mouth. Dual contact increases tool- holder rigidity for improved performance especially at extended gauge lengths The HSK contacts the spindle taper and flange on the spindle face to make a solid union in both the axial and radial planes. In operation, HSK tool holders are resistant to axial movement because the face contact prevents the toolholder from being pulled up into the spindle at high speed. Cutting tools generally takes higher radial forces because the flange contact and taper contact combine to resist deflection. DrawbarThe HSK drawbar "fingers" reach inside the Hollow Shank. One of the big advantages of HSK is the "Merry go Round" effect on the drawbar fingers and how centripetal forces affect it. As the RPM is increased on the HSK toolholder the drawbar fingers actually use become a tighter connection on the inside of the flange and increase the pressure in the spindle connection. February 2023 Editors note: New graphics and minor editing and corrections have been made to this article to improve the readability. The old graphic element has been moved here to the bottom of the screen while everything above has been recreated with higher resolution (non blurry) elements.
14 Comments
|
Technical Support BlogAt Next Generation Tool we often run into many of the same technical questions from different customers. This section should answer many of your most common questions.
We set up this special blog for the most commonly asked questions and machinist data tables for your easy reference. If you've got a question that's not answered here, then just send us a quick note via email or reach one of us on our CONTACTS page here on the website. AuthorshipOur technical section is written by several different people. Sometimes, it's from our team here at Next Generation Tooling & at other times it's by one of the innovative manufacturer's we represent in California and Nevada. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
About
|
© 2024 Next Generation Tooling, LLC.
All Rights Reserved Created by Rapid Production Marketing
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
