|
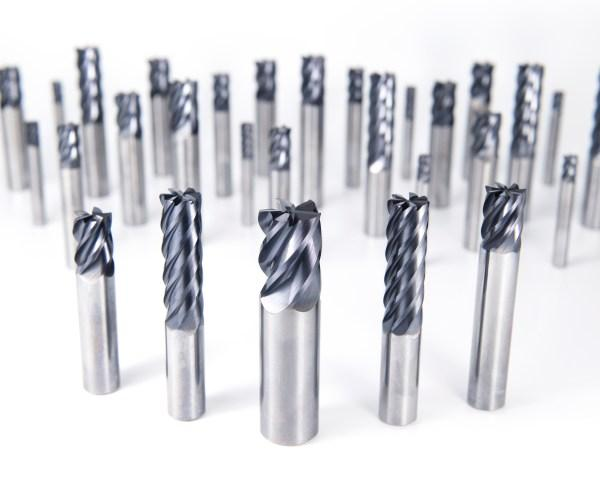
by Peter Jacobs, via OSG USA blog There are almost as many distinct variations of CNC tools as there are finished products that could be milled. If you are familiar with the functions these tools perform, it will be much more straightforward for you to select the ones appropriate for the project you are working on. When it comes to the amount of time it takes and the quality of the work to be produced, choosing the appropriate cutting tool for your CNC milling machine, the material, and the type of milling can have a significant impact. So here is a list of prominent milling tools utilized for CNC cutting. Different types of CNC milling tools make it feasible to achieve the highest level of product customization. While cutting into and shaping different types of materials, several tools are employed. The tool that should be utilized to cut also gets decided by the finalized design of the cut. Aside from these factors, specialists choose their tools based on how well they match the required speed with the desired finish. Depending on the ultimate purpose of the completed product, one of these two considerations might take precedence over the other. The top 7 milling tools for CNC cutting are: 1. End MillsThere are numerous kinds of end mills, each of which is designed for a particular kind of cutting. All end mills cut at an angle of ninety degrees. A center-cutting end mill is what's required to make a vertical cut. These mills can cut both the center and the margins of the workpiece. Non-center cutting end mills feature a hole in the middle of the tool and only contain cutting edges mostly along the ends of the mill. Since roughing end mills have fewer flutes than standard end mills, they are the tools of choice for making the initial cuts in a workpiece. You will need finishing end mills with additional flutes to obtain a design similar to the part you want to produce. It will enable you to deliver a component that is cut with immense precision. The tool employed on a project will vary depending on several factors, the most important of which is the number of flutes and the material of its composition. The production of end mills typically involves the use of cobalt, high-speed steel, and carbide as raw materials. More details about the different types of mills (as per their material) are given below.
End mills may perform a wide variety of cuts, the type of tool used depends on the type of cut being made:
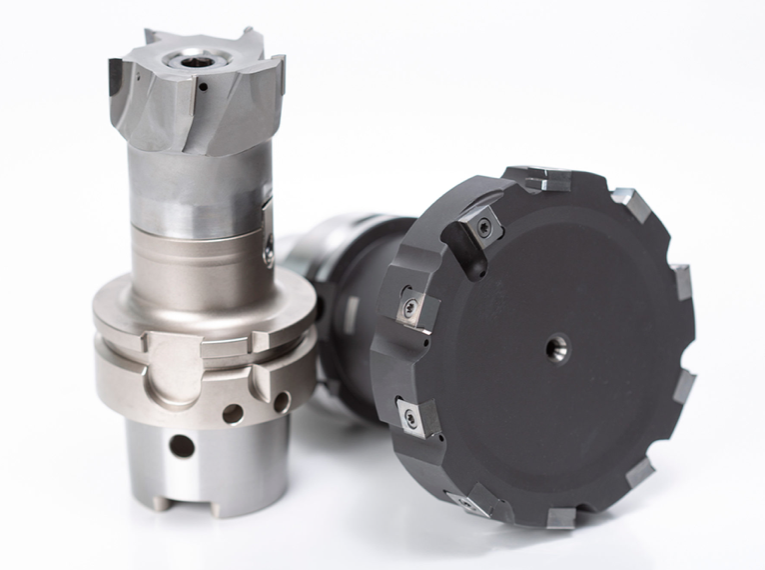
2. Face MillsThis tool is primarily used to create a level surface on a solid portion of the material. As the first step in milling, this is often performed on the top of the stock to smooth it out. The cutter inserts in a face mill's sole body can be changed for specialized cutting tasks. You would require more cutters to remove metal at a faster rate. 3. Twist DrillsDrill bits resemble end mills in that they have a conical cutting tip on the end of a shaft with one or even more flutes. Twist drills are often made from solid carbide or High-Speed Steel (HSS). The drill's hardness, wear resistance, and lifespan can be improved by applying a gold-colored coating, such as TiN. 4. Fly CuttersFly cutters are considered the best to create a fantastic surface finish. The clockwise motion of these cutting tools produces a mirror-like finish on the material. 5. Center Spotting DrillsThese stocky tools first construct a precise conical hole to avoid the drill bit from drifting during a cutting operation and end up drilling the hole at an incorrect site. Screw clearance holes and counterbores can be drilled with the same tool thanks to multi-function drills that spot and countersink. 6. ReamersReamers are mainly utilized to enlarge the existing holes in compliance with the tolerance while providing a superior surface finish. They help you ensure the accuracy of the roundness and diameter of a drilled hole. For reamers to work, a pilot hole of roughly the same diameter as the final product must first be bored. 7. Taps and Thread MillsTaps are tools used to cut threads into the interior of a material. Yet not every thread is produced by a cutting procedure. By applying pressure, Roll Form taps get inserted into holes, and the surrounding material is shaped to fit them. Thread mills are similar but can be employed to cut internal or external threads. Concluding RemarksThe key to successfully machining products and components is selecting the appropriate CNC tool. Learn how each one functions, and keep in mind the use of the most beneficial ones in your manufacturing facility. About the AuthorPeter Jacobs is the Senior Director of Marketing at CNC Masters. He is actively involved in manufacturing processes and regularly contributes his insights for various blogs in CNC machining, 3D printing, rapid tooling, injection molding, metal casting, and manufacturing in general.
1 Comment
Mapal's FaceMill-Diamond-ES & NeoMill-T-Finish exact an optimum surface finish for every quantity of parts With an extensive and diversified range of tools for reaming, drilling and milling and many years of process experience, MAPAL places a huge focus on aluminium machining. Two new products address additional customer requirements:
Both of these increase economic efficiency in aluminum milling applications. FaceMill-Diamond-ES – the versatile PCD face milling cutter is ideal for small quantities
The milling cutters have fewer cutting edges than the established FaceMill-Diamond tools, making them a more cost-effective and an “Economical Solution”. With a diameter of 50mm (1.96"), for instance, the FaceMill-Diamond-ES has five cutting edges, while the classic FaceMill-Diamond has twelve. Another difference is the area of application: The FaceMill-Diamond-ES is suitable for shoulder milling, trimming and machining thin-walled parts, as well as face milling. The new milling cutter is available in the diameter range of 32mm(1.26") to 80mm (3.15"). Dimensions have not changed in comparison to existing FaceMill-Diamond models. Accordingly, it can be used directly in existing production, if, for example, the larger chip space of the new tools should be used. Cutting depths of up to 10 mm are easily possible. All milling cutters in the FaceMill-Diamond-ES series can be reground and re-equipped. They are exclusively available as milling cutters for arbor mounting. NeoMill-T-Finish – finishing aluminium with indexable inserts
With the new system, customers can also use other cutting materials in addition to the PCD-tipped inserts, depending on application and workpiece material, such as uncoated carbide or carbide with CVD diamond or PVD coating. This means the optimum cutting material can be used for aluminium workpiece materials with different silicon content and casting processes (sand casting, pressure die casting and permanent mould casting).
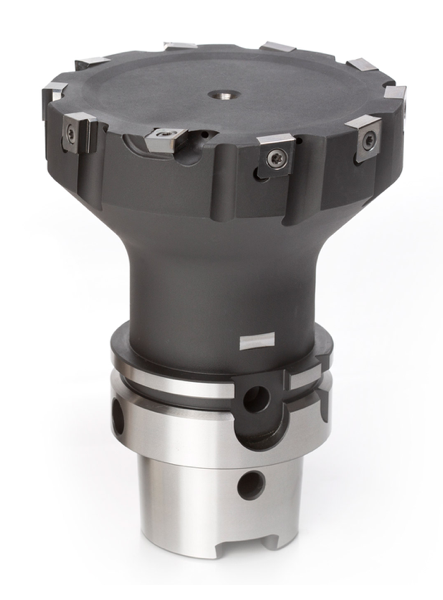
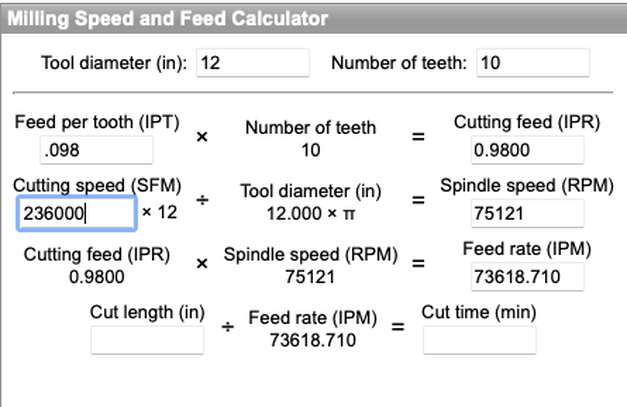
The indexable inserts each have up to four usable cutting edges. An optimum version is available for every customer and every requirement, offering maximum economic efficiency and process reliability. A patent-pending insert arrangement system is what makes the new milling cutter unique. The main inserts, which perform stock removal of up to 2.5mm (0.98"), are attached to the circumference. A wide finishing insert arranged axially is responsible for the ability to reach surface roughness levels of Rz = 1.5 µm. The innovative system enables homogeneous wear and tear on the cutting edges: Thanks to the special arrangement of main inserts and wide finishing inserts, all main inserts have the same feed per tooth, smooth running for good surface quality and no burr formation. The resulting longer tool life is reflected in a lower cost per part with a high level of process reliability. Each tool is adapted specifically to the customer’s requirements. Maximum economic efficiency and productivity are the top priority. The tool body is usually made from steel. If weight restrictions are in place, MAPAL manufactures the tool body in aluminum or with a weight reduction bore. The NeoMill-T-Finish can be configured in the diameter range from 50mm (1.97") to 315mm (12.4") and can be ordered as a monolithic unit or an adaptive unit for milling holders with arbor. Cutting speeds of up to 6,000m/min (236,220IPM) and feed rates of 2.5mm (0.98" IPR) per revolution are possible in use. |
Technical Support BlogAt Next Generation Tool we often run into many of the same technical questions from different customers. This section should answer many of your most common questions.
We set up this special blog for the most commonly asked questions and machinist data tables for your easy reference. If you've got a question that's not answered here, then just send us a quick note via email or reach one of us on our CONTACTS page here on the website. AuthorshipOur technical section is written by several different people. Sometimes, it's from our team here at Next Generation Tooling & at other times it's by one of the innovative manufacturer's we represent in California and Nevada. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
About
|
© 2024 Next Generation Tooling, LLC.
All Rights Reserved Created by Rapid Production Marketing
|





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
