|
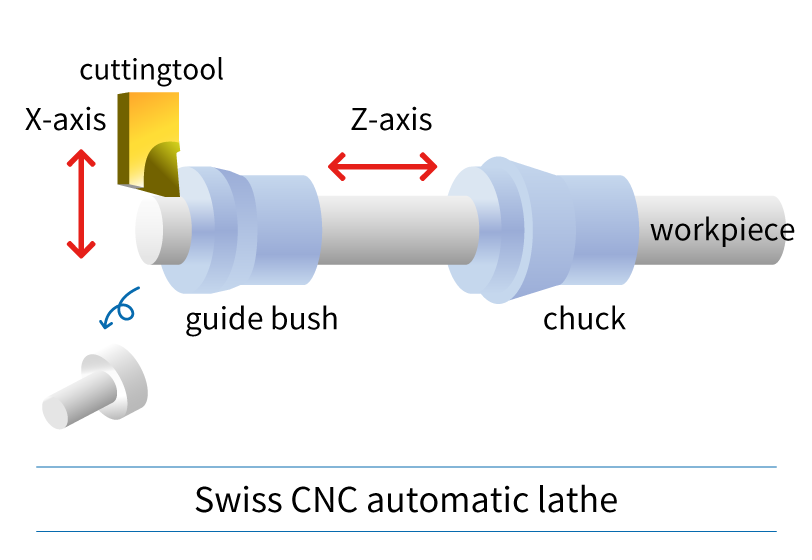
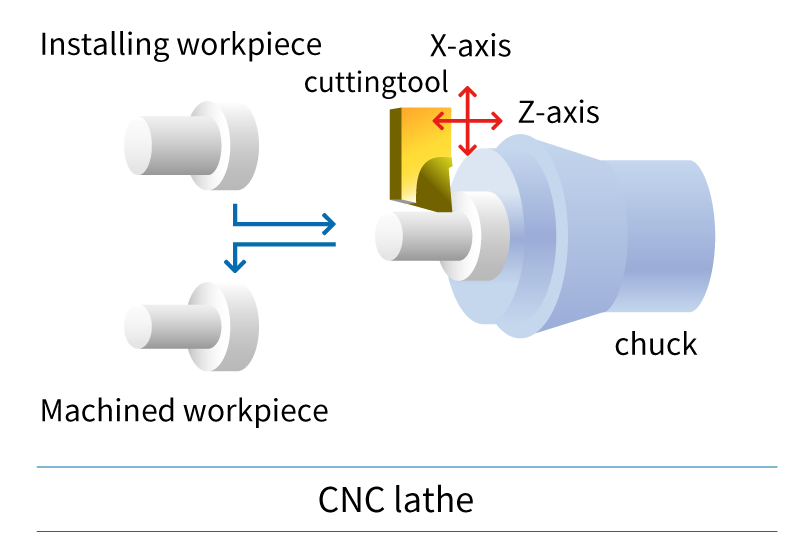
A Swiss type CNC automatic lathe and a CNC lathe, they are similar lathe machines, but did you know they are completely different? In this article, the kind folks at NTK Cutting Tools will introduce the 4 differences between the cutting tools used based on the mechanical structure of Swiss CNC automatic lathes and CNC lathes. What is the difference between a “Swiss CNC Automatic Lathe” and a “CNC lathe”?
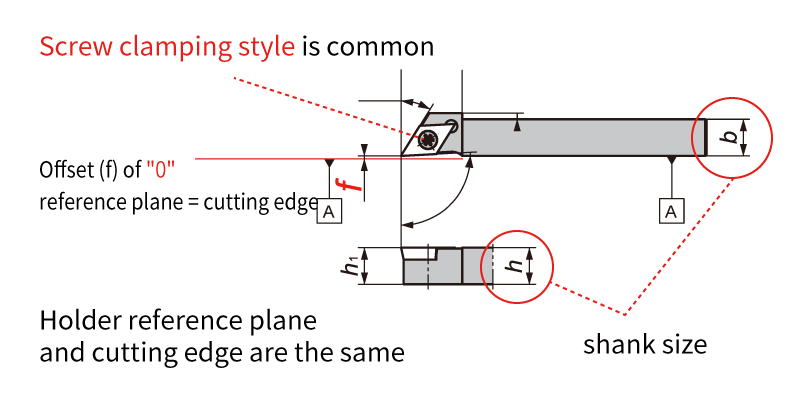
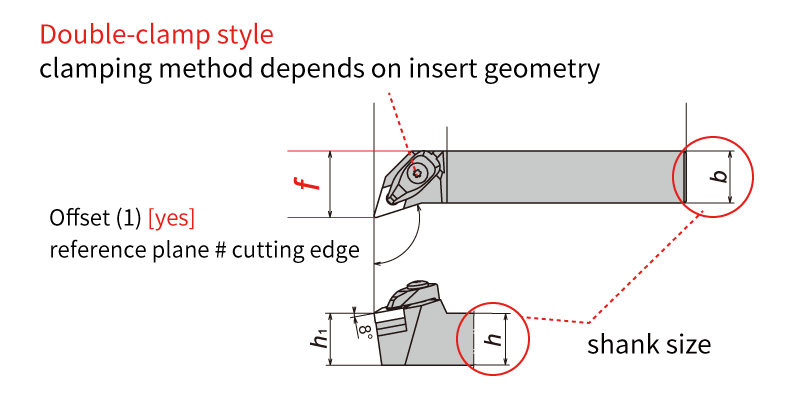
Swiss CNC automatic lathe & CNC lathe: Since the machine structure, workpiece, and size are different, it is important to select the cutting tool accordingly. Now let's take a look at the features of cutting tools used in CNC automatic lathes. Difference 1. HolderThe holder is an important component for achieving chip performance. I will explain the difference between the holder used on a Swiss type CNC automatic lathe and a CNC lathe. Holders for Swiss CNC Automatic Lathe
CNC Lathe Holders
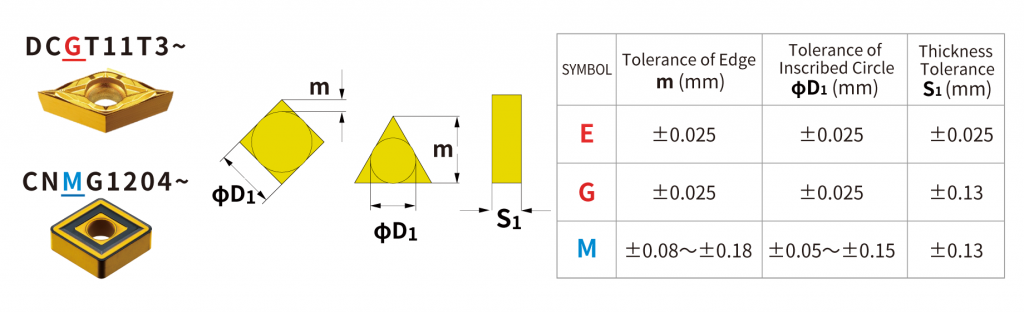
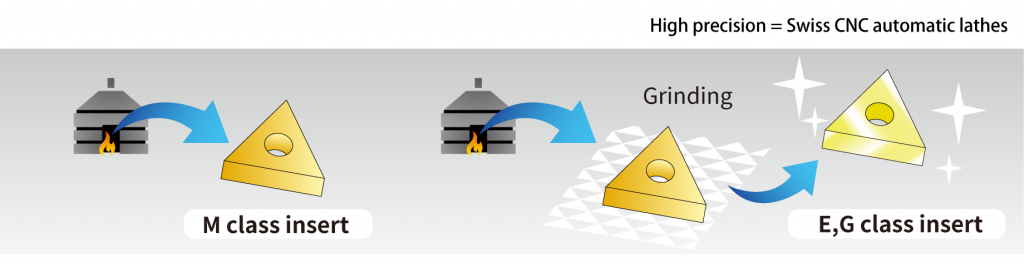
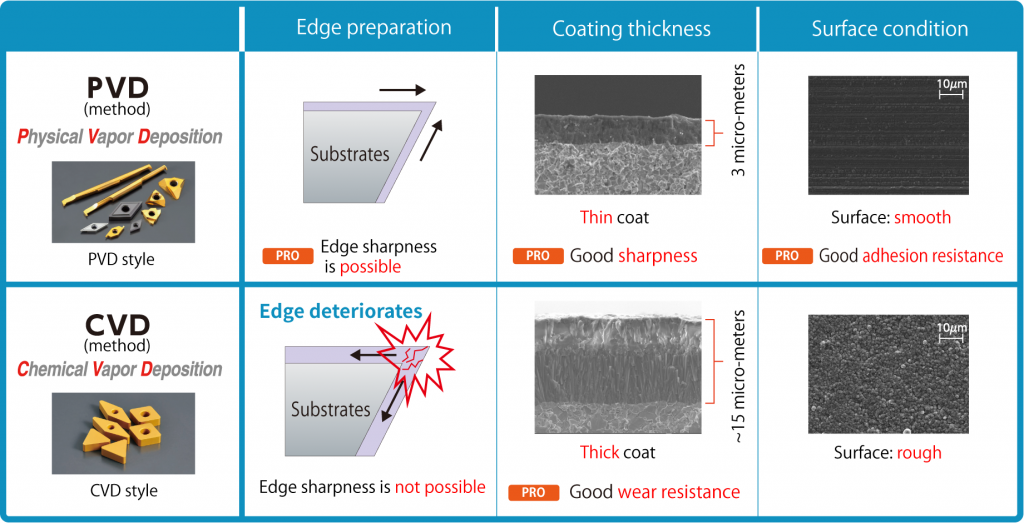
Difference 2. Insert geometry: Positive inserts and Negative insertsCNMG... DNMG...: If you are familiar with machining on CNC lathes, you likely know about insert geometries. The Swiss type CNC automatic lathe is the same type of lathe, but if you are thinking of machining with the same insert, be careful! Inserts such as "CNMG /CNGA..." and "DNMG/DNGA ..." used on CNC lathes have many corners, and the cutting edge is honed or chamfered (edge preparation) and have excellent cutting edge strength. These inserts are ideal for shearing the workpiece material. On the other hand, when a negative insert such as "CNMG/CNGA..." is used on a Swiss type CNC automatic lathe, cutting resistance tends to be high and "chatter" and "work deflection" occur. We recommend using a "positive style" for Swiss CNC automatic lathes. Swiss-type CNC automatic lathes machine workpieces that are smaller in diameter and require higher precision than machining on a CNC lathes. High cutting resistance causes “vibration” and “dimensional defects”, so using a “positive insert” with a relief angle to reduce cutting resistance and achieve stable machining. b Difference 3. Insert tolerance: G-class and M-classThe table above compares the “M” class commonly used on CNC lathes with the “G” class and “E” class commonly used on Swiss SNS automatic lathes. The 3rd letter in the insert part description identifies the tolerance class. Insert such as CNMG… and DNMG… have an M class tolerance. On the other hand, inserts such as DCGT… and CCGT… have a G-class tolerance. As shown in the table, the insert tolerance is very different between the “G” and “M” class. Corner length (m) and insert IC (dia. D1) tolerance affect the accuracy of the cutting edge position, or workpiece dimensions. Thickness tolerance (S1) affects the height of the cutting edge. Swiss-type CNC automatic lathes require high precision machining of small diameter workpieces, so “G-class” or “E-class” with higher tolerance than M-class are used. Also, the upper and lower insert surfaces of G-class and E-class inserts are polished and the outer edges are ground with high accuracy which achieves excellent sharpness. For Swiss CNC automatic lathes, it is strongly recommended to use inserts with “G-grade” and “E-class” tolerances. Difference 4. Coatings types: PVD vs. CVDCoating is an important factor in determining the performance of tools and the quality of workpieces. There are two main types of coatings - CVD and PVD. Which coating is suitable for Swiss CNC automatic lathes? Inserts like “CNMG” and “DNMG” used on CNC lathes are generally CVD coated. CVD coatings can be thick films compared to PVD coatings and have excellent abrasion resistance. But, because it is a thick film coating, it is easy to cause deterioration and there is a disadvantage of a rough coating surface. Swiss-type CNC automatic lathe machining requires high precision, sharpness is important, so PVD coatings are more suitable due to thin film coatings achieving sharp edges. As shown in the figure above, PVD coatings have excellent sharpness, dimensional stability, and welding resistance making it the ideal coating style for Siwss-type CNC automatic lathes. Do you still have questions about the difference between tooling used for a Swiss type CNC lathe and traditional CNC lathe?
NTK offers a large lineup of tools specialized for CNC automatic lathes. If you are having issues machining, please consider contacting us for technical advise.
4 Comments
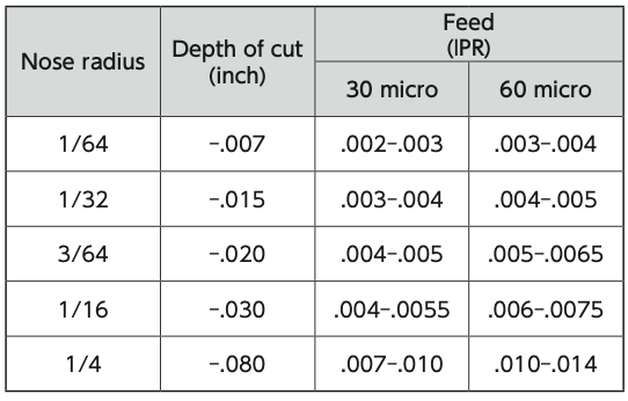
Here are some simple quick tips when you are machining machining hard materials.
Tough, Precise, and Fast —Carmex HBA carbide grade is available today for tomorrow’s materials10/21/2020 As more applications require the use of super-hard alloys, manufacturers are demanding tooling that can deliver precision threads and high production in less time. To meet these challenges, Carmex Precision Tools Ltd. has engineered carbide grade HBA — an extra-fine, submicron grade with high toughness for optimized performance on hardened steel Titanium and super alloys including Hastelloy, Inconel and Nickel base alloys up to 62 HRc. Available for internal and external threading in both 60° and 55° partial profile, as well as ISO metric and UN, HBA delivers high wear and heat resistance and excellent edge stability. The unique combination of carbide substrate, coating type and edge conditions provide superior performance over extended tool life. Case Study in Threading D2 at 53-56HRc In a recent test involving an external right-hand thread:
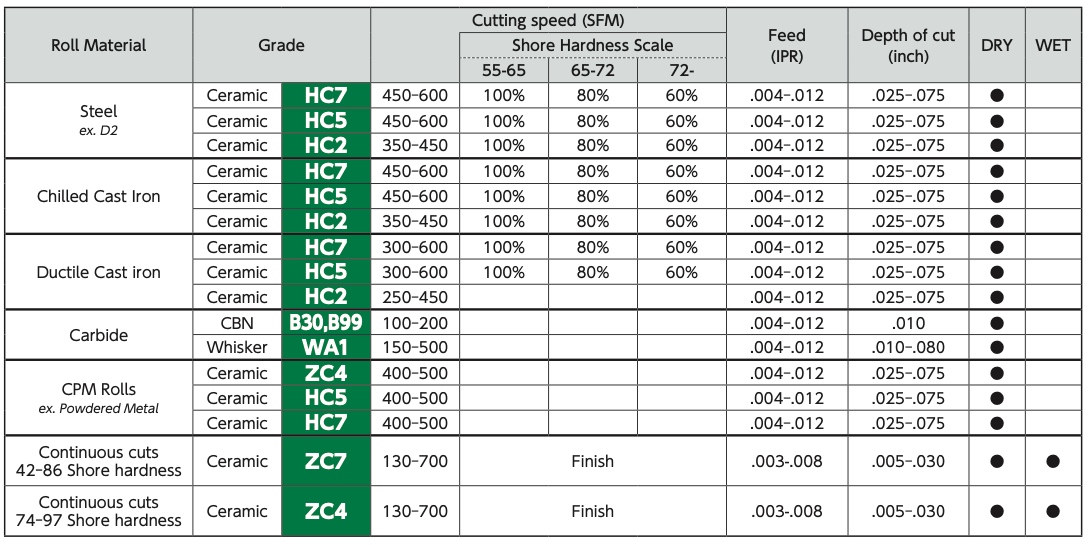
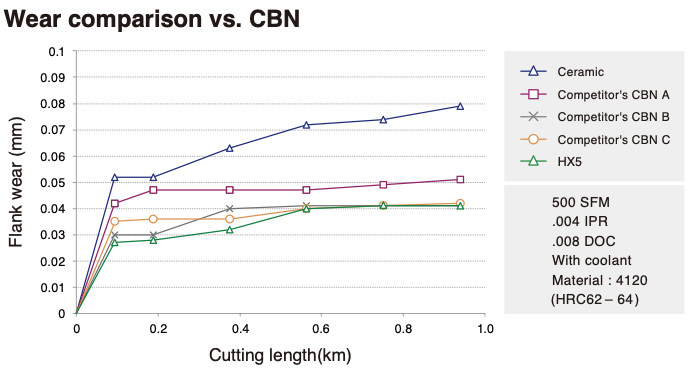
Hard machining is increasingly becoming the rule rather than the exception in complex part production. Carmex HBA was engineered to meet the challenges inherent in threading hard materials while delivering high production and longer tool life. Bring us your most challenging hard threading applications and lets try the new Carmex HBA engineered performance carbide . NTK CeramiX HX5 replaces CBN NTK developed this latest game changing ceramic material NTK CeramiX HX5 to replace CBN. As a ceramic cutting tool specialist, NTK has been researching new advancements for ceramics in the industry for decades. They recently introduced a new grade that matches CBN on performance. The new CeramiX "HX5" grade provides a cost saving solution for hard turning applications. It's designed for Hard Turning with continuous cut in the Hardness range of 55 to 66HRc
|
Technical Support BlogAt Next Generation Tool we often run into many of the same technical questions from different customers. This section should answer many of your most common questions.
We set up this special blog for the most commonly asked questions and machinist data tables for your easy reference. If you've got a question that's not answered here, then just send us a quick note via email or reach one of us on our CONTACTS page here on the website. AuthorshipOur technical section is written by several different people. Sometimes, it's from our team here at Next Generation Tooling & at other times it's by one of the innovative manufacturer's we represent in California and Nevada. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
About
|
© 2024 Next Generation Tooling, LLC.
All Rights Reserved Created by Rapid Production Marketing
|







 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
